|
IN BRIEF
|
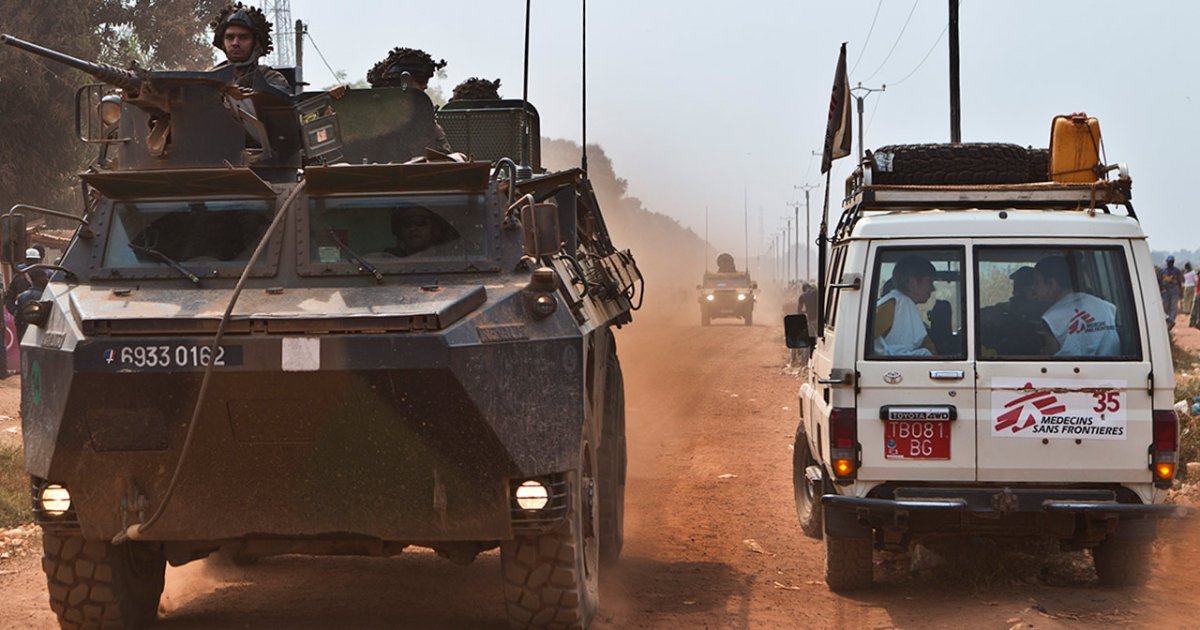
Understanding the organization chart Doctors Without Borders (MSF) is essential to understand how this international humanitarian organization operates on a daily basis. Founded in 1971 in Paris, MSF relies on coordinated teams who work on the ground to provide medical aid to populations in distress. With its 25 sections spread across the world, each level of the organizational chart plays a crucial role in the implementation of humanitarian missions. By dissecting this structure, we can better appreciate the commitment and effectiveness of this NGO in its interventions on the ground.
When we think of humanitarianism, Doctors Without Borders (MSF) occupies a prominent place thanks to its unwavering commitment to populations in distress. But how does this valuable organization really work? By exploring its organizational chart, we can better appreciate its structure and internal mechanisms, while identifying the benefits And disadvantages of its configuration.
Benefits
The first strong point of the MSF organization chart lies in its decentralized structure. With 25 sections and several operational centers around the world, the organization benefits from great flexibility in the management of its interventions. This allows teams to quickly adapt to local needs and respond effectively to humanitarian crises.
In addition, the distribution of responsibilities within the organization chart facilitates quick decision making. Indeed, regional coordinations are close to the field and can therefore act without wasting time, a precious asset when people’s lives are at stake.
Finally, the fact that MSF is based on a democratic governance allows them to remain faithful to their founding values. The participation of teams in the decision-making process helps to strengthen adherence to the organization’s missions and to guarantee the integrity of actions carried out in the field.

Mondial Assistance reaches 1.5 billion euros in turnover in 2007 and prepares for future growth
In 2007, Mondial Assistance reached a historic milestone by reaching €1.5 billion in revenue. This milestone marked a turning point in the company’s expansion, and the company was already planning its future growth paths. In a sector where innovation is…
Disadvantages
Despite its many strengths, the Médecins Sans Frontières organizational chart is not without challenges. In fact, the decentralization, while beneficial, can also create inconsistencies in the implementation of guidelines and the sharing of best practices between different sections. This can lead to disparities in the quality of support provided.
Another notable disadvantage is the administrative complexity which can sometimes slow down certain operations. The existence of multiple levels of hierarchy and the need for coordination between different teams can hinder the effectiveness of interventions in emergency situations where every minute counts.
Finally, the importance of maintaining independent funding can make MSF vulnerable to economic fluctuations and changes in donor generosity. This can lead to financial responsibilities which directly affect the organization’s ability to carry out its humanitarian missions.
In this article, we will guide you through the organization chart of Doctors Without Borders (MSF), an international humanitarian medical aid organization founded in 1971. You will discover how this structure is organized to maximize its effectiveness on the ground and meet the needs of populations in distress around the world. This understanding will allow you to understand how MSF operates and its main challenges.

Choosing the right mutual insurance for expatriates in Asia
Embarking on an expat life in Asia is an exhilarating adventure, filled with cultural discoveries and professional opportunities. However, a crucial question quickly arises: how can you ensure adequate health coverage that protects both your well-being and your budget? Whether…
An international organization
Doctors Without Borders emerged from a pioneering initiative, bringing together doctors and journalists in Paris in 1971. Over time, MSF expanded to become an international association having 25 sections and international representation. This geographic diversity allows the organization to intervene quickly and effectively in humanitarian crises, while respecting local realities.

Boursorama Banque and Revolut: financial services duel in 2025
Boursorama Banque and Revolut are emerging as essential pillars of modern financial services. While Boursorama Banque perpetuates its heritage of reliability and French banking tradition, Revolut represents the breakthrough of a bold British neobank with innovative features. Their duel promises…
Headquarters and coordination teams
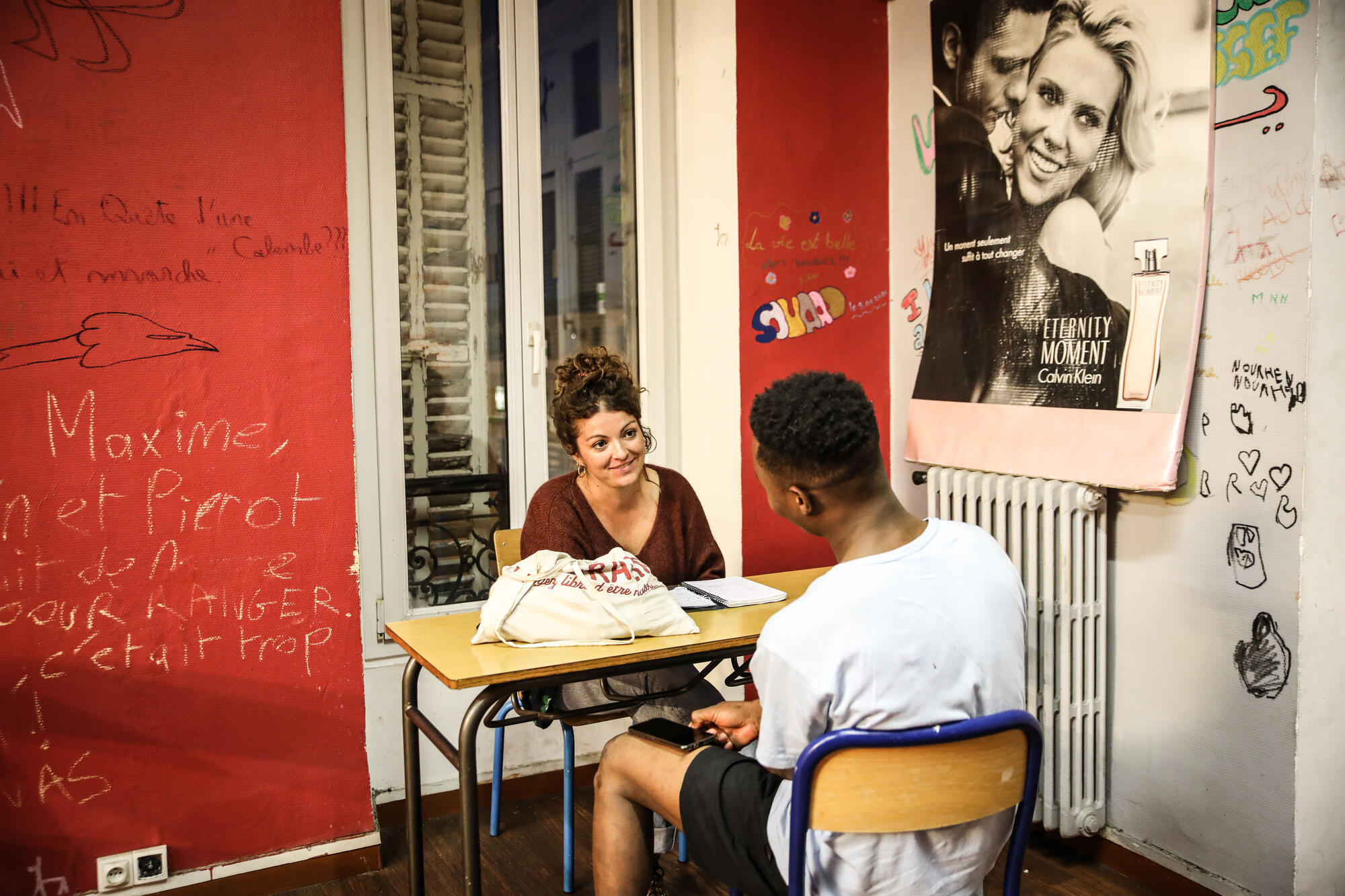
At the heart of this organization, the seat plays a crucial role. He manages operations and provides support to coordination teams in the field. These teams, based in the capitals of the countries of intervention, are responsible for planning and executing missions. To learn more about MSF operations management, you can consult informative resources like this page.

Discover LovExpat: the first dating app dedicated to French expats
Expat life is a unique adventure, marked by the challenges of adapting to a new culture, creating new social networks, and sometimes, finding a romantic connection. LovExpat, the app born from the vision of two French sisters, addresses this need.…
Operational centers
MSF is structured around five operational centers who coordinate interventions on the ground. These centers, located in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Geneva, London and Nairobi, are decisive for the effectiveness of humanitarian missions. Each center manages specific regions and works closely with local teams to ensure a rapid and relevant response. More information about this structure is available at our site.

AgoraExpat – Your Reliable Ally for Expatriate Medical Coverage
Living in a foreign country is an enriching adventure, but it also comes with unique challenges, particularly when it comes to healthcare. Navigating a new healthcare system can be complex and worrying. Therefore, the need for reliable and comprehensive medical…
Management principles
Management within MSF is based on key principles that guarantee effective decision-making. This process is characterized by the practical wisdom, THE management through deliberation and the principle of subsidiarity. Thanks to these values, each member of the organization is encouraged to contribute during strategic reflections, making the system more dynamic and inclusive. Find out more about these management practices by consulting this blog.
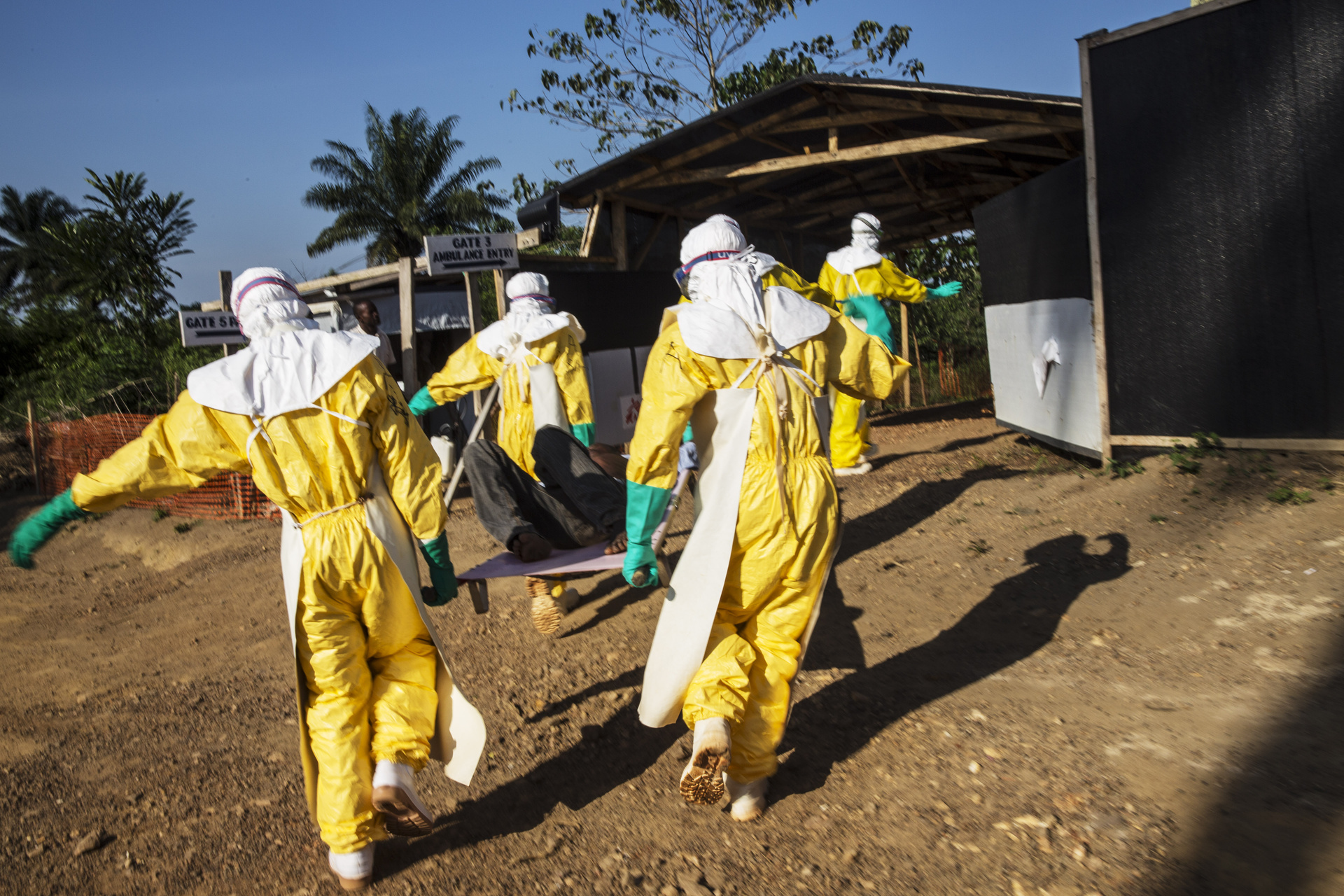
Humanitarian commitment
Doctors Without Borders embodies an unwavering commitment to populations in distress. Each intervention is guided by humanitarian values that prioritize access to medical care, independence, and neutrality. MSF’s mission is not limited to providing care, but also aspires to advocate and raise awareness about humanitarian crises on a global scale.
To understand the organization chart of Doctors Without Borders (MSF), it is essential to understand how this international humanitarian organization works. MSF, founded in 1971 in Paris by a group of doctors and journalists, is made up of 25 sections, each playing a key role in assisting populations in distress. In this article, we will explore the organizational structure and how each level contributes to the effectiveness of the humanitarian aid provided by MSF.
The structure of the organization
At MSF, the structure is divided into several levels in order to effectively manage field operations. At the top is the international representation which establishes guidelines and coordinates the actions of the different sections. Each national section acts autonomously while remaining in contact with the international headquarters. This allows MSF to be responsive and flexible to the needs of populations affected by crises.
The role of headquarters
THE seat of MSF plays a fundamental role in the management of operations. He coordinates interventions by providing logistical support and strategic advice to teams in the field. This centralized structure ensures consistency in the actions carried out while respecting local specificities. Each section is also supported by experts in areas such as public health, there logistics and the communication, thus guaranteeing a multidisciplinary approach.

Understanding first euro health insurance in France
IN BRIEF Health insurance at 1st euro : international coverage for expatriates. Support for health costs from the first euro spent. Independent of the Fund for French people abroad (CFE). Reimbursement to 100% without excess (depending on the formula chosen).…
Operational centers
MSF has five operational centers who supervise interventions in different regions of the world. These centers are located in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Geneva, Nairobi and Brisbane. Each operational center ensures the management and coordination of humanitarian missions in its geographical area. They ensure that the specific needs of populations are met while maintaining the standards of eradication and access to care, fundamental principles of MSF.
The teams on the ground
At the heart of MSF’s action are teams on the ground, made up of doctors, nurses and other health professionals, who work directly with affected populations. These teams are the essential link between the organization and the beneficiaries of the aid. They face daily challenges, ranging from geographic isolation to unstable security conditions, but their unwavering commitment remains the cornerstone of MSF’s interventions.
Communication and engagement
Finally, Meyer would not be MSF without a strong emphasis on communication and the resource mobilization. The organization works to raise public awareness of humanitarian crises and the need for rapid response. Transparent reporting on the use of funds and mission results helps build trust and to encourage continued donor support.
To find out more about how this organization works, you can visit the page Who are we ? or find out how to act with MSF by visiting MSF: from headquarters to the field.
| Flowchart Elements | Description |
| Seat | Coordinates and supervises all field missions. |
| Sections | 25 entities that manage specific projects in different countries. |
| Coordination teams | Responsible for managing local operations and supporting teams in the field. |
| Operational centers | Five centers around the world, each overseeing distinct missions. |
| Medical staff | Includes doctors, nurses and other healthcare professionals. |
| Volunteers | Support for specific tasks during emergency interventions. |
| Local partners | Collaboration with NGOs and local authorities for better efficiency. |

The structure of Doctors Without Borders (MSF) is designed to optimize the efficiency of its operations in the field. It starts with a central headquarters that plays a crucial role in the management and coordination of humanitarian missions. This headquarters, located in Paris, supervises the actions of the different sections, ensuring that each team has the necessary resources to act quickly when required.
At the operational level, MSF has five centers strategic locations across the world: Amsterdam, Barcelona, Geneva, London and Nairobi. Each center is in charge of specific missions in its geographical areas of influence. This distribution allows the organization to respond to emergencies with agility and mobilize medical teams where they are most needed.
The teams in capital play a direct role in ensuring that field operations run smoothly. This includes research missions, intervention planning and human resources management. The coordinators of these teams work hand in hand with the medical teams, thus guaranteeing constant communication and responsiveness adapted to the needs of the populations on the ground.
With its rich history since its creation in 1971, MSF has been able to evolve while maintaining its commitment to humanitarian values. THE professionals who make up this organization, ranging from doctors to logisticians, ensure that interventions comply with the MSF charter, which is based on the principles of solidarity and independence. Each actor has a well-defined role and contributes to the overall mission of the organization.
At the NGO level, staff management, training and updating protocols are an integral part of operations. The importance of participative management at MSF ensures that all voices are heard, thus promoting a climate of exchange and collaboration. This ensures that each decision taken is in line with the realities on the ground, while maintaining the human objective at the heart of the organization’s actions.
To understand how coordinated and effective the humanitarian commitment of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) is, it is essential to delve into its organizational chart. This structure, which is structured around different sections and international connections, allows the organization to carry out its medical aid missions while adapting to local contexts. In this article, we will explore the different components of MSF, highlighting the importance of each part in the overall functioning of the organization.
MSF National Sections
MSF is made up of 25 national sections, each with its own office and management team. These sections are responsible for the strategy, financing and implementation of operations in their geographic area. For example, the French section, which is one of the oldest, plays a major role in planning operations on the ground.
Role of Sections
Each section provides human and financial resources to support the organization’s projects. This means that the medical teams, logisticians and other professionals are often mobilized locally, thus providing a rapid and adapted response to crises. This decentralization allows MSF to benefit from a diversity of skills and knowledge that enriches the entire organization.
Operational Centers
In addition to the sections, MSF has five operational centers which are the heart of interventions on the ground. These centers are located in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Geneva, Paris and Nairobi. Their primary mission is to coordinate operations and ensure that the specific needs of affected areas are identified and addressed.
Coordination of Interventions
Operations centers play a crucial role in planning missions, sending teams into the field and managing the necessary resources. Through their liaison with the national sections, they ensure that interventions are not only rapid but also effective, ensuring that the medical services and humanitarian relief arrives where it is most needed.
International Management
At the head of MSF, a international management coordinates all activities and ensures compliance with the fundamental values of the organization. It also ensures the link between the different sections and operational centers, guaranteeing cohesion in the decisions taken and the actions carried out.
Vision and Strategy
International management sets strategic objectives and ensures that each section and operational center works in harmony towards these objectives. His role is essential to maintaining MSF’s humanitarian vision and to ensuring that the organization remains true to its commitment to the most vulnerable.
Partnership with Local Actors
Another fascinating aspect of MSF’s organizational chart is its engagement with local stakeholders. In collaboration with local NGOs, health authorities and communities, MSF ensures that its actions are adapted and respectful of the cultural, social and political realities of the affected regions.
A Collaborative Approach
This collaborative approach allows MSF to strengthen the impact of its interventions, drawing on the knowledge and experience of local populations. Ultimately, this promotes better crisis management in the long term, because the solutions provided are often better understood and accepted by those who benefit from them.

To understand the organization chart of Doctors Without Borders, it is essential to grasp the unique structure that allows this humanitarian organization to operate in an efficient and coordinated manner. Created in 1971 in Paris by doctors and journalists, MSF has evolved to adapt to the complex challenges of humanitarian aid around the world.
At the heart of this organization, we find 25 sections who work to carry out medical and humanitarian missions. Each of these sections, while having its own functioning, is linked to an international representation. This allows MSF to benefit from great flexibility and the ability to adapt to crises that arise.
THE operational centers, located in Amsterdam, Barcelona, Geneva and other cities, play a key role in coordinating interventions on the ground. These centers are responsible for project management, logistics and assessing needs in the field. They support teams who, often in emergency situations, respond to the needs of populations in distress.
MSF’s management model is based on principles such as decentralization and the participation. Each member of the organization, whether in the field or at headquarters, is encouraged to express their ideas and contribute to decision-making. This promotes an environment where local initiatives can emerge, making the organization even more relevant and effective in its missions.
In short, the organization chart of Médecins Sans Frontières clearly illustrates the complexity and richness of this organization, which deploys its expertise while remaining close to the realities experienced by victims of crises around the world.
FAQ about the Médecins Sans Frontières organization chart
Who founded Médecins Sans Frontières? Médecins Sans Frontières was created in 1971 in Paris by a group of doctors and journalists wishing to provide humanitarian medical aid independently.
What is Médecins Sans Frontières? It’s a non-governmental organization (NGO) of French origin which offers humanitarian medical aid throughout the world, particularly in response to health crises and conflicts.
How many sections does Médecins Sans Frontières make up? Médecins Sans Frontières is organized in 25 sections across the world, each playing a key role in managing operations.
What are the operational centers of Médecins Sans Frontières? The organization has five operational centers who coordinate interventions on the ground: Amsterdam (OCA), Barcelona (OCBA), Geneva (OCG), and others to come.
What is the function of Médecins Sans Frontières headquarters? Headquarters manages all operations, providing valuable support to field teams and ensuring the coordination of humanitarian actions.
How is the coordination team in the field organized? There coordination cell works closely with headquarters to implement projects and interventions in affected countries.
What principles guide the operation of Médecins Sans Frontières? The organization is governed by ethical principles such as independence, neutrality and impartiality in providing assistance to populations in distress.
How are members of Médecins Sans Frontières recruited? Recruitments are based on a rigorous process that evaluates candidates’ experience, skills and commitment to the organization’s humanitarian values.



